C++ 构造函数 析构函数
4256 点击·0 回帖
一、整体代码 Test.h
[cpp] #ifndef _TEST_H_ #define _TEST_H_ class Test { public: // 如果类不提供任何一个构造函数,系统将为我们提供一个不带参数的 // 默认的构造函数 Test(); Test(int num); void Display(); ~Test(); private: int num_; }; #endif // _TEST_H_ Test.cpp [cpp] #include "Test.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; // 不带参数的构造函数称为默认构造函数 Test::Test() { num_ = 0; cout<<"Initializing Default"<<endl; } Test::Test(int num/*=0*/) { num_ = num; cout<<"Initializing "<<num_<<endl; } Test::~Test() { cout<<"Destroy "<<num_<<endl; } void Test::Display() { cout<<"num="<<num_<<endl; } 01.cpp [cpp] 01.cpp #include "Test.h" int main(void) { Test a; a.Display(); Test a2(10); Test a4 = 10; a2.Display(); Test* a3 = new Test(20); // new operator a3->Display(); delete a3; int b; int b2(2); int b4 = 2; int* b3 = new int(38);// delete b3; Test c[2] = {10, 20}; Test* c2 = new Test[2]; delete[] c2; int d[2]={10,20}; int* d2 = new int[2]; delete[] d2; return 0; } 二、运行结果 图片:94704.jpg 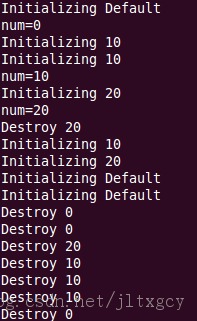
三、解释 Test a; Test* a3 = new Test(20); 第一个是在栈内存分配了空间,第二个是在堆内存分配了空间,第一个随着作用域的结束,而调用析构函数,第二个必须要手动delete,才能调用析构函数。 析构函数没有返回值,不能重载。 构造函数可以重载,但是重载后默认构造函数就没有了。 系统提供空的构造函数和析构函数。 缺省参数的构造函数,Test(int num=0),和Test()重复了,如果Test t 就不知道调用哪个了。 | ||